Receptor design
T cell therapies entail genetically modifying individual's immune cells to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) or antigen-specific T cell receptors (TCRs). Once re-introduced into the individual’s body, they guide the immune system to identify and destroy tumor cells.
Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) design
CARs are cell surface structures that bind to antigens on target cells. When expressed on cytotoxic immune cells– such as T cells or NK cells–CARs can help direct them to kill cancer cells.
CAR T-cells are one approach to immunotherapy wherein T cells are removed from an individual and then genetically modified to contain CARs to target surface antigens on tumors for eradication.
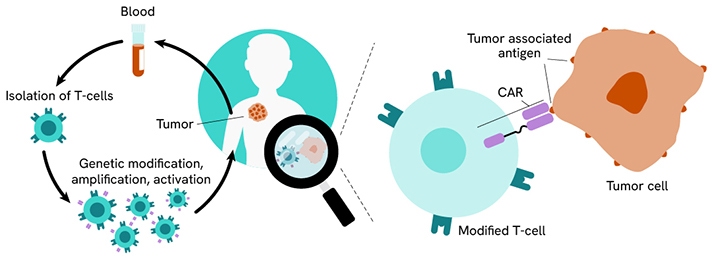
CAR T-cell therapy workflow.
CAR design consists of an extracellular domain, typically a single-chain variable fragment (scFv) from a monoclonal antibody to recognize the tumor antigen, a linker or spacer followed by a transmembrane domain (e.g. CD3ζ), and an intracellular signaling domain that acts in a stimulatory fashion to the T cells (e.g. CD28, or 4-1BB) to facilitate destruction of the cancer cells.
A common method for scFv discovery is hybridoma screening. Hybridoma screening for CAR generation involves immunizing mice, creating hybridomas, and identifying specific antibodies. The variable regions are sequenced, linked to form scFvs, and tested for antigen binding. Successful scFvs become part of CAR-T cells, directing them to target and destroy cancer cells with precision.
Revvity offers a selection of HTRF™ and AlphaLISA™ anti-tag reagents that can be used for hybridoma screening. For more information, read our article, “Therapeutic antibody discovery: screening and characterization strategies for the newest classes of therapeutic antibodies.”
Are you interested in novel types of cell therapies? Read this white paper to discover the benefits of CAR NK-cell therapy, “Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) Natural Killer cells - a promising cell therapy strategy for cancer treatment.”
Monitor T cell activation
Monitoring T cell activation is important for ensuring the therapeutic efficacy and safety of cell therapies, as activated T cells are effective at targeting cancer cells.
The T cell receptor (TCR) initiates a signaling cascade, involving transcription factor activation and cytoskeletal remodeling, resulting in T cell activation.
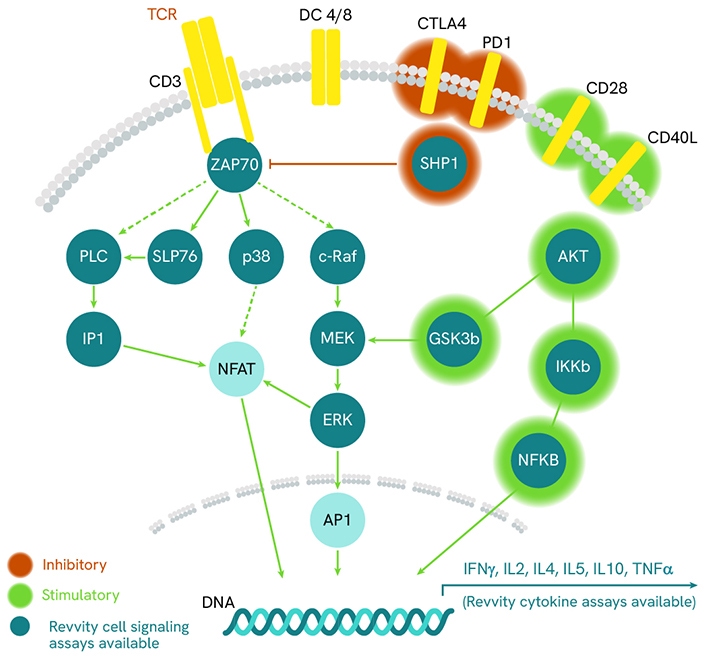
TCR signaling pathway.
TCR engagement triggers the phosphorylation of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) on the cytoplasmic side of the TCR/CD3 complex. This event recruits ZAP70 to the TCR/CD3 complex, where it is subsequently phosphorylated and activated promoting recruitment and phosphorylation of downstream adaptor or scaffold proteins, including SLP-76. Activated SLP-76 translocates to the plasma membrane and promotes a multi-protein complex, which participates in the activation, survival, and proliferation of T lymphocytes. Additionally, signals from other cell surface receptors, such as CD28, further modulate the cellular response.
Phosphorylated Protein Detection
Revvity offers a vast portfolio of no-wash cellular protein phosphorylation assays to study specific and ubiquitous signaling proteins associated with TCR signaling pathways and cell activation in both primary cells and cell lines.
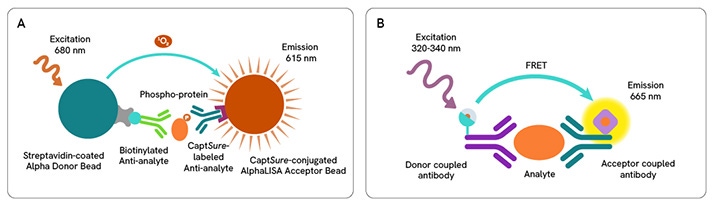
A: AlphaLISA SureFire® Ultra™ technology uses Donor beads coated with streptavidin and Acceptor beads coated with a CaptSure agent. The proximity of Donor and Acceptor beads in the presence of phosphorylated protein generates a luminescent signal proportional to the amount of target protein.
B: HTRF technology uses two labeled antibodies to generate a FRET signal, which is directly proportional to the concentration of analyte in the sample.
AlphaLISA SureFire® Ultra™ and HTRF (Homogeneous Time Resolved Fluorescence), provide you with additional benefits like ease-of-use, scalability, and the absence of washing, without compromising on sensitivity and specificity.
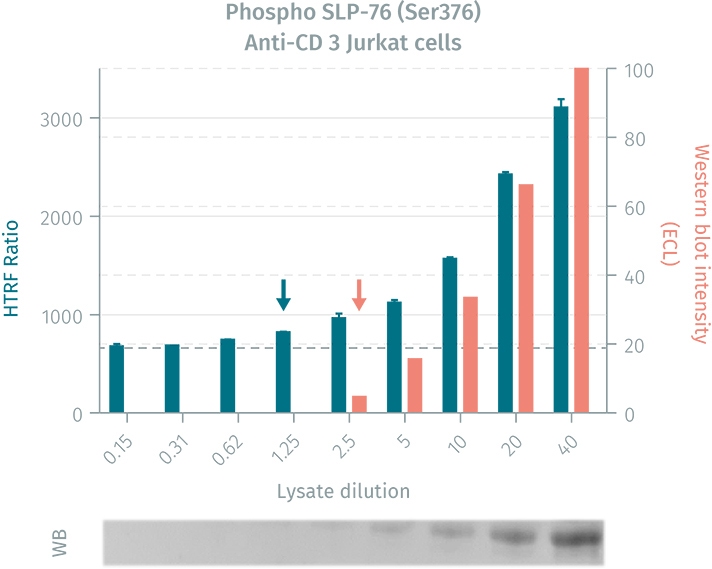
Comparison of the HTRF phospho-SLP-76 cellular assay to a western blot on lysates prepared from human Jurkat cells.
Cytokine Detection
When T cells are activated, they release a variety of cytokines. Some of the key cytokines released include: Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α), Interleukin-2 (IL-2), Interleukin-4 (IL-4), Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Interleukin-10 (IL-10) and Interleukin-17 (IL-17). These cytokines play a crucial role in immune response: activating and directly other immune cells, enhancing cell-mediated cytotoxicity, and driving an inflammatory response.
These signaling molecules can be measured in the supernatant by immunoassays such as AlphaLISA and HTRF. These methods might be used for measuring cytokine molecules associated with T cell activation while consuming minimal sample and providing efficient time-to-results.
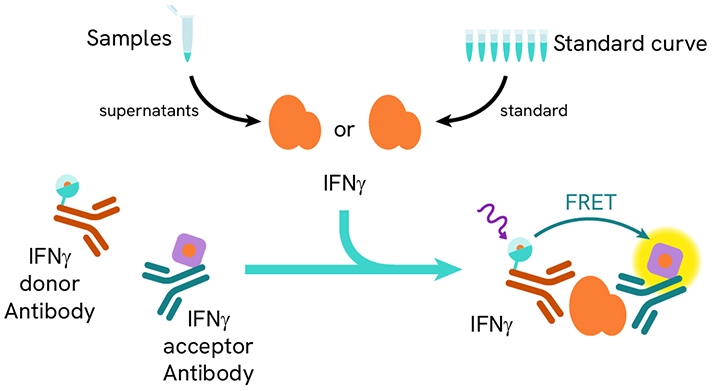
HTRF IFN-γ assay principle.
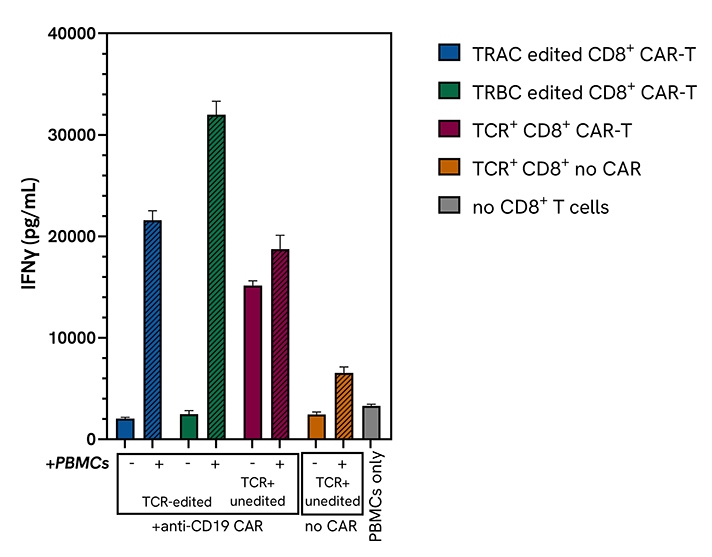
Functional validation of CD8+ CAR T cells using the HTRF IFN-γ assay: isolated primary CD8+ T cells were engineered with an anti-human CD19 CAR lentivirus, after high-efficiency knock-out of the endogenous TCR α/β utilizing the top performing Dharmacon Edit-R TRAC or TRBC sgRNAs. These TCR-negative (TCR-) CD8+ CAR T cells were functionally characterized using a variety of methods, including the HTRF Human IFN-γ kit.
Download this application note to see how HTRF phospho assays in primary models can take your experiments further!
Download this application note to learn more about Dharmacon’s Edit-R platform can be used with Revvity’s immunoassays for CAR-T engineering and characterization.
Learn more about how our immunoassays can be used to monitor cytokine release from immune cells: download this application note now!
Assess potency
Functional potency assays are used to assess the capability of engineered T cells to identify and eradicate cancer cells. In vitro bioassays for cell killing are used to evaluate the cytotoxic activity of immune cells and the potential effect of new therapeutics on immune cell killing activity.
Cytokine production
Cytokines are key mediators of the immune and inflammatory systems and are often used as markers to assess how a drug candidate modulates biological functions. Reproducible, accurate and robust methods for quantifying cytokine release are necessary for the development and quality control of cell therapies.
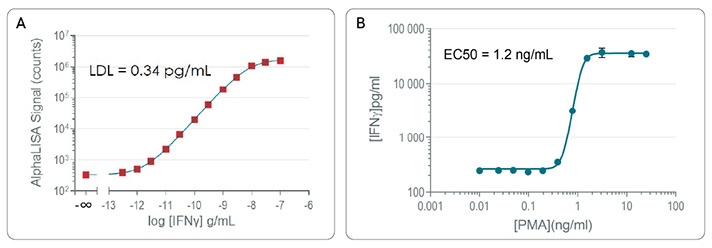
A: AlphaLISA High Performance standard curves for detection of IFN-γ in cell culture media (RPMI + 10% FBS).
B: Stimulation of cytokine release: IFN-γ secretion post-PMA/ionomycin treatment.
Revvity provides a portfolio of no-wash immunoassays to quantify cytokines such as IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-10, and TNF-α in many different sample types.
Targeted cell killing
To directly assess cell killing, Revvity offers a non-radioactive alternative to Cr-51 release assay with use of the DELFIA™ (dissociation-enhanced lanthanide fluorescence immunoassay) cell cytotoxicity assay kit, designed to measure cell-mediated cytotoxicity. The assay has also been used for antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC).
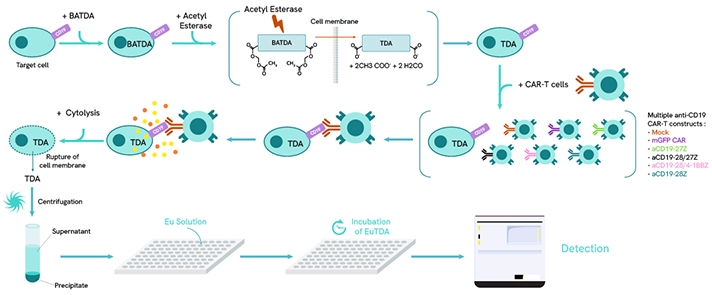
DELFIA EuTDA Cytotoxicity Assay in a CAR T-cell co-culture format. After loading target cells with BATDA reagent, the cells rapidly process the molecule into TDA and are then co-cultured with the selected CAR T-cell line. Activation of the CAR T-cells leads to cytokine release and cytolysis of the target cell line. TDA is then collected in the supernatant and mixed with a Europium solution to form EuTDA which is highly fluorescent. The final level of EuTDA is proportional to the amount of cell death from the target cell population. Maximum release control wells are used to calculate specific release and are established by using lysis buffer to fully lyse the target cells.
Learn more about using our DELFIA kit.
Read this literature review focuses on monitoring CAR-T cell activation and their cytotoxicity.
Discover this application note about simultaneous measurement of chemokine/cytokine release and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity upon binding with rituximab.
Quantify total viral capsid titers
Development of safe, reliable, and efficient gene transfer vectors is one of the keys to successful gene therapy. Two vehicles for gene transfer are the Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) and Lentiviral Vectors (LVs). To help with the development of your vector-based gene therapies, we offer a portfolio of no-wash immunoassays to quantify AAV and LV titers.
Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) vectors
Despite challenges like manufacturing scalability and the presence of neutralizing antibodies, Adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors, derived from a non-pathogenic virus, are promising
- Dive into AAV vectors challenges for gene therapy manufacturing in this white paper.
Revvity provides a range of immunoassays that detect and quantify AAV capsid (in Viral Particles per milliliter - VP/mL) utilizing AlphaLISA technology and HTRF technology. The AAV Capsid Detection Kits are available for AAV1, AAV2, AAV3B, AAV5, AAV6, AAV8 and AAV9 serotypes, and can measure AAV particles present in cell culture media, lysis buffer and cell lysate.
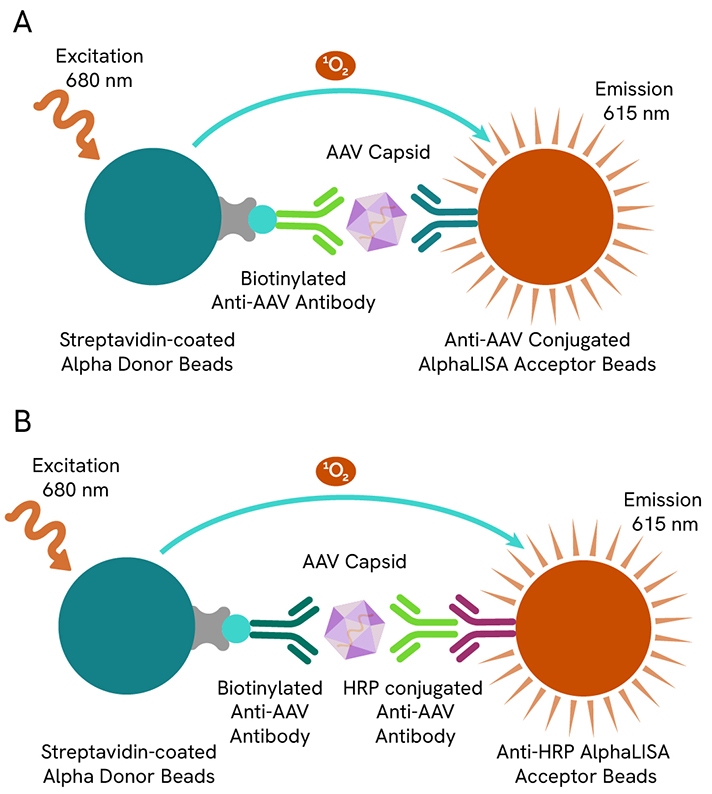
A: Canonical AlphaLISA AAV capsid detection kit.
B: AlphaLISA AAV1 & AAV6 capsid detection kit.
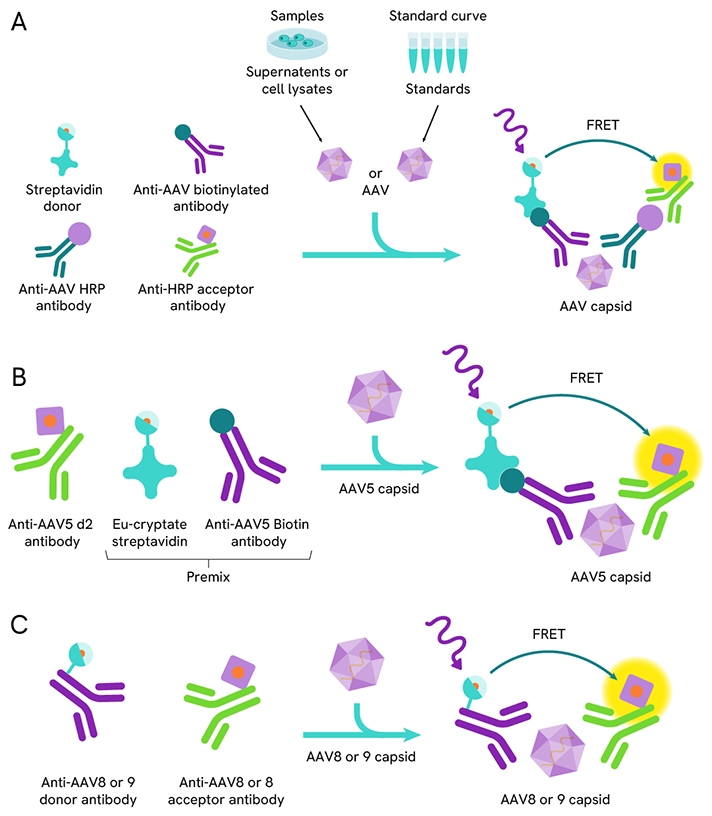
Detection of the AAV capsid using HTRF AAV capsid detection kits.
A: Assay scheme for HTRF AAV1, AAV2, AAV3B and AAV6 capsid detection kits.
B: Assay scheme for HTRF AAV5 capsid detection kit.
C: Assay scheme for HTRF AAV8 and AAV9 capsid detection kits.
Learn more about these reliable and accurate no-wash HTRF and AlphaLISA AAV immunoassays in these application notes.
Lentiviral vectors
Lentiviruses (LVs) are RNA-based viruses capable of stable transgene integration in target cell genomes, making them effective for gene transfer. They are used in both ex vivo gene therapy, where cells are modified outside the body and re-infused, and in vivo gene therapy, where LVs are directly injected into individuals.
The HIV p24 protein is engaged in the assembly, maturation, and disassembly of HIV/HIV-derived lentiviral vectors and is used commonly implemented to deliver transgenes to mammalian cells. Assays against HIV p24 antigen have become a common method for measuring lentiviral transduction efficiency.
Revvity offers HTRF and AlphaLISA HIV p24 detection kits which can be used to monitor transduction efficiency.
- HTRF HIV p24 Detection Kit (64P24PEG, 64P24PEH)
- AlphaLISA High Sensitivity HIV p24 Detection Kit (AL291C, AL291F)
- AlphaLISA Biotin-Free HIV p24 Detection Kit (AL332HV, AL332C, AL332F)
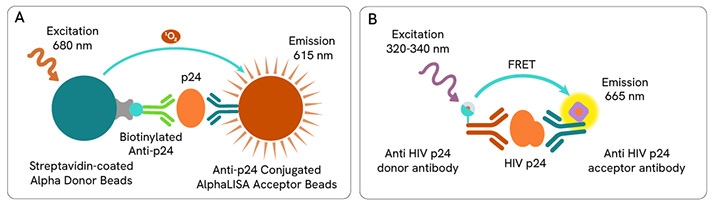
A: AlphaLISA p24 assay principle.
B: HTRF p24 assay principle.
Read this application note entitled, “A comparative study of two immunoassay platforms to determine lentivirus titer for CAR-T development.”
Bioprocess contaminant detection
HEK293 HCP
Host cell proteins (HCPs) are impurities from host organisms, like bacteria, yeast, or mammalian cells, introduced during the production of Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) or recombinant proteins. The clearance of these contaminants, especially from Human Embryonic Kidney (HEK) 293 cells used in gene therapy, is crucial due to potential negative clinical effects and reduced product effectiveness.
Revvity designed the AlphaLISA HEK293 HCP detection kit (AL3198C) to measure contaminants from the HEK293 cells. Learn more in this application note entitled, “Streamline the HEK 293 HCP impurity quantification workflow with new, no-wash AlphaLISA HEK 293 Host Cell Protein Kit.”
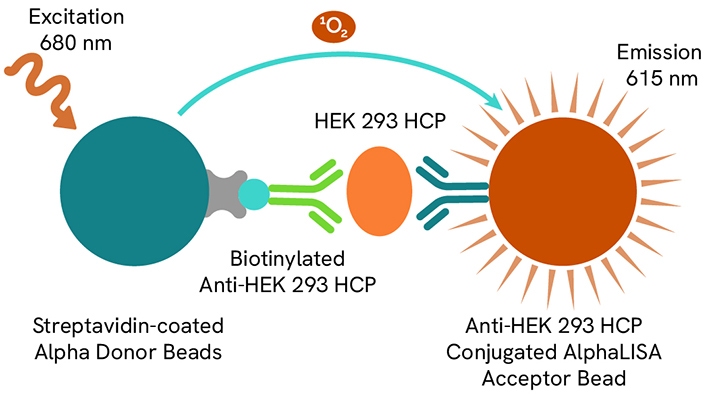
AlphaLISA HEK HCP detection kit assay principle.
IVT dsRNA
In Vitro Transcription (IVT) is a molecular biology technique that creates RNA sequences from a DNA template using RNA polymerase and ribonucleotides. Although the aim is to produce single-stranded RNA (ssRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) can also form as a byproduct.
IVT is mainly used in gene therapy and mRNA vaccine development. dsRNA contaminants must be carefully managed due to their immunogenicity, which can trigger severe immune responses. Thus, a reliable method for quantifying dsRNA is essential during IVT purification to ensure its effective removal.
Revvity offers an HTRF dsRNA (IVT) kit (64DSRNAPEG) intended for the detection of dsRNA in such IVT samples.
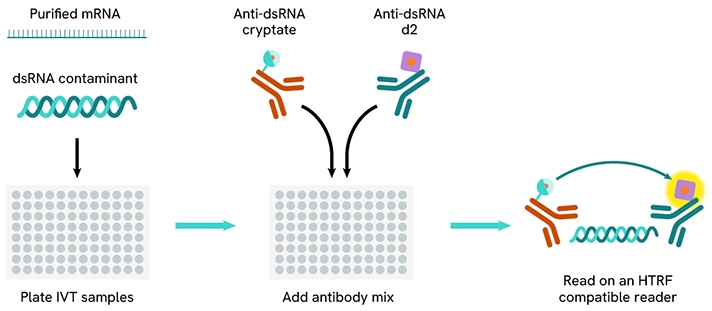
HTRF dsRNA (IVT) assay workflow.
Featured resources
































