Rheumatoid arthritis
Dive deeper into understanding rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is considered as the most common chronic inflammatory disease. This autoimmune disease affects around 1% of the global population and is more prevalent in females than males.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic and symmetric inflammatory disease associated with joint redness, hotness, stiffness, swelling and pain. Affected joints are primarily located at the wrists, fingers, toes, and knees.
The rheumatoid arthritis inflammatory pathway
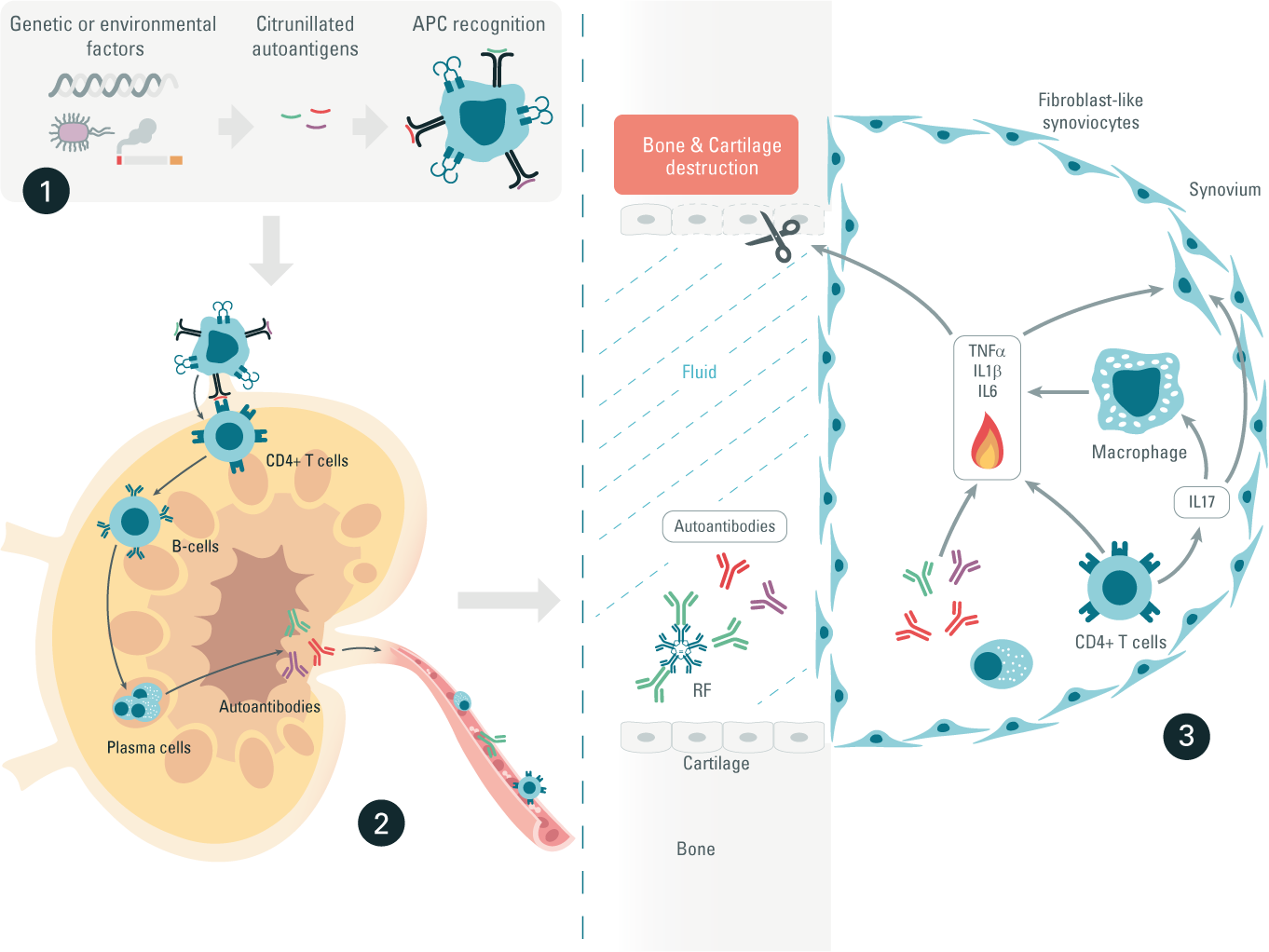
Step 1: Triggers are of genetic or environmental origin, or both, causing a phenomenon known as peptide citrullination. Citrunillation is a post-translational modification that converts arginine into citrulline. Citrunillated proteins are then considered as foreign antigens and are recognized by antigen-presenting cells (APCs).
Step 2: Autoantigen loaded-APCs migrate into the lymph nodes, where they activate CD4+ helper T-Cells. In turn, these helper T-cells stimulate B-cell differentiation into plasma cells, which produce autoantibodies. The two most important autoantibodies associated with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA).
Step 3: CD4+ helper T cells, plasma cells, RF, and ACPA autoantibodies migrate through the bloodstream and infiltrate back into joints. We then observe an activation of immune cells in joints, triggering cytokine production. Over the long-term, this autoimmune reaction in RA can result in cartilage damage and bone erosion.
Systemic lupus
Boost your research on systemic lupus disease
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease mediated by autoantibodies and immune complexes. SLE is a chronic multisystem disorder mainly affecting women between 15 and 40 years of age. It is estimated that at least five million people worldwide have some form of lupus. This number could be much higher, as SLE is difficult to diagnose.
Symptoms associated with SLE include fatigue, weight loss, and fever. UV-sensitive butterfly rash across the nasal bridge occurs in 50% of SLE patients and represents the most common sign of SLE.
The lupus inflammatory pathway
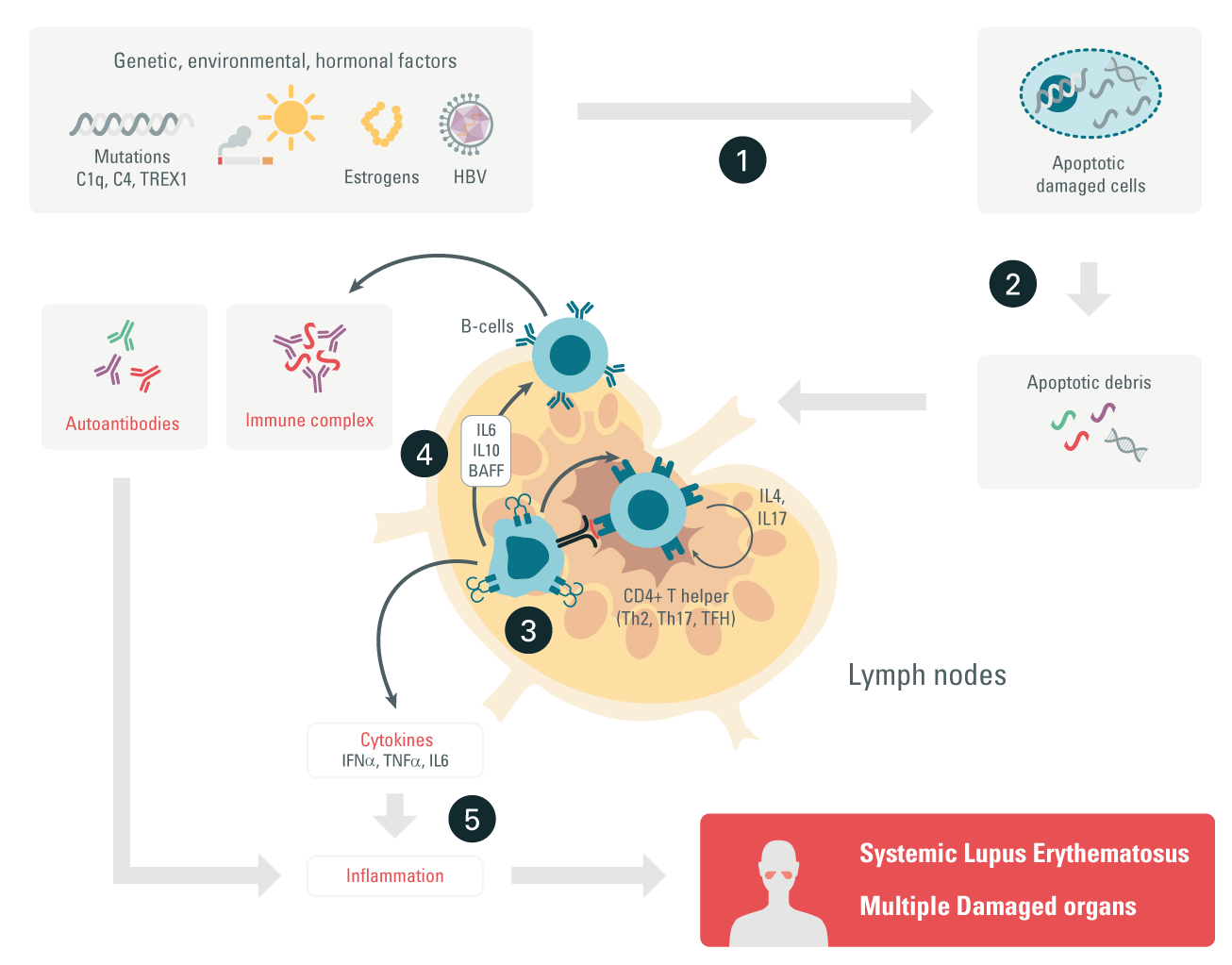
Step 1: Researchers believe that a complex and combined interaction of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors trigger enhanced cell death (apoptosis).
Step 2: Apoptosis triggers the release of apoptotic debris. The debris is taken up by APCs or activates neutrophils, which trigger a cascade resulting in tissue damage and the formation of thrombosis.
Step 3: Activated APCs present the autoantigens to T cells, which produce pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Proinflammatory cytokines can induce tissue damage.
Step 4: In turn, T cells activated by autoantigens can activate B cells, which start producing autoantibodies that form immune complexes (ICs) with the autoantigens.
Step 5: When ICs settle in tissue, they start recruiting inflammatory cells, leading to tissue damage.
Inflammatory bowel disease
Discover how Revvity’s immunoassays rise to the IBD research challenge
Characterized by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is divided into two related diseases: Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). UC is a continuous superficial inflammation that spreads from the distal to the proximal colon. It is mainly localized in the rectal and sigmoid colon. CD is a discontinuous inflammation affecting the different cellular layers of the gastrointestinal tract, mainly the ileocecal area, small intestine, and colon.
It often appears in young adults between 15 and 40 years of age.
IBD inflammatory pathway
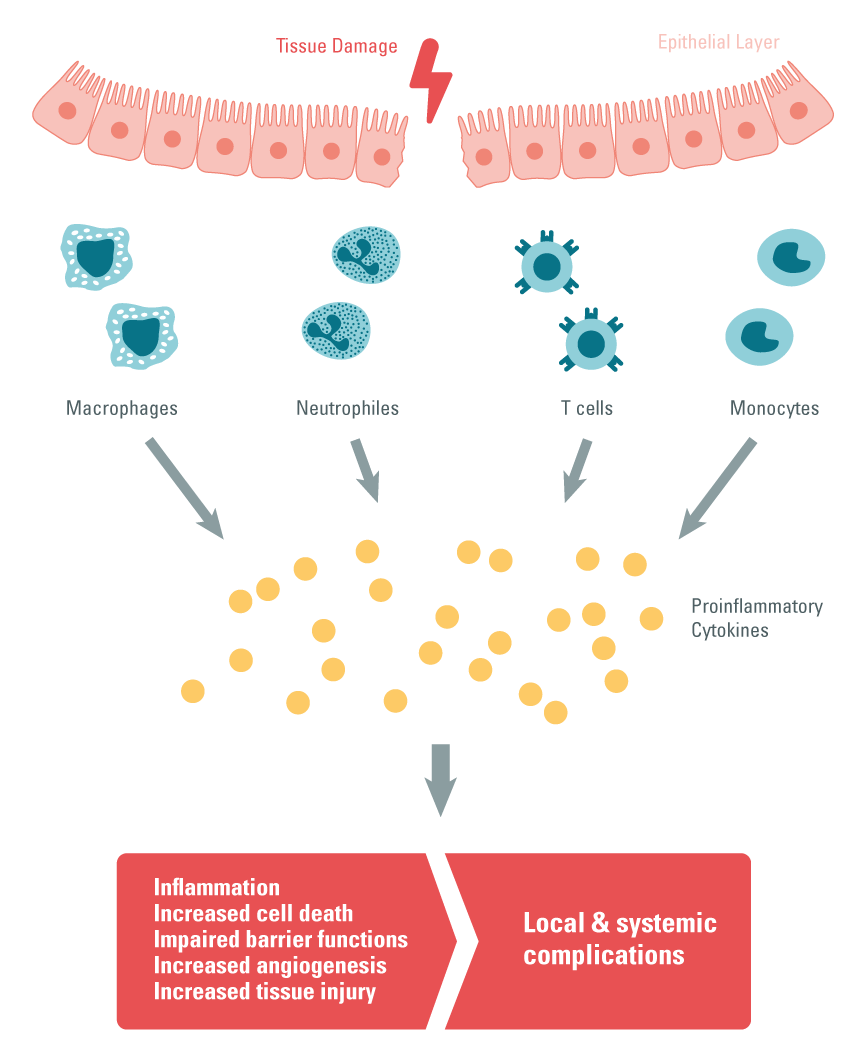
Step 1: Lesions in the intestinal epithelial layer increase intestinal permeability, which triggers excessive infiltration of immune cells and results in tissue damage.
Step 2: After the infiltration of immune cells (monocytes, macrophages and T cells) in the gastrointestinal tract, proinflammatory cytokine production can be observed. Th17 cells play a central role, as they also produce proinflammatory cytokines and recruit neutrophils and macrophages to damaged tissue.
Step 3: Under duress, intestinal epithelial cells are responsible for the expression of pattern recognition receptors (PPRs) called TLRs. This pathway is also a source of proinflammatory cytokine production.
Step 4: The hyperactivation of TLRs causes chronic inflammation in IBD patients 14.
Multiple sclerosis
Tackling multiple sclerosis research
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic organ-specific autoimmune disease targeting the central nervous system (CNS). MS is associated with neuroinflammation resulting in a progressive demyelination process and neuronal damage. Relapsing-remitting and secondary progressive MS (RRMS, SPMS) are the two most frequent forms of MS, predominantly affecting women between 20 and 40 years of age.
MS inflammatory pathway
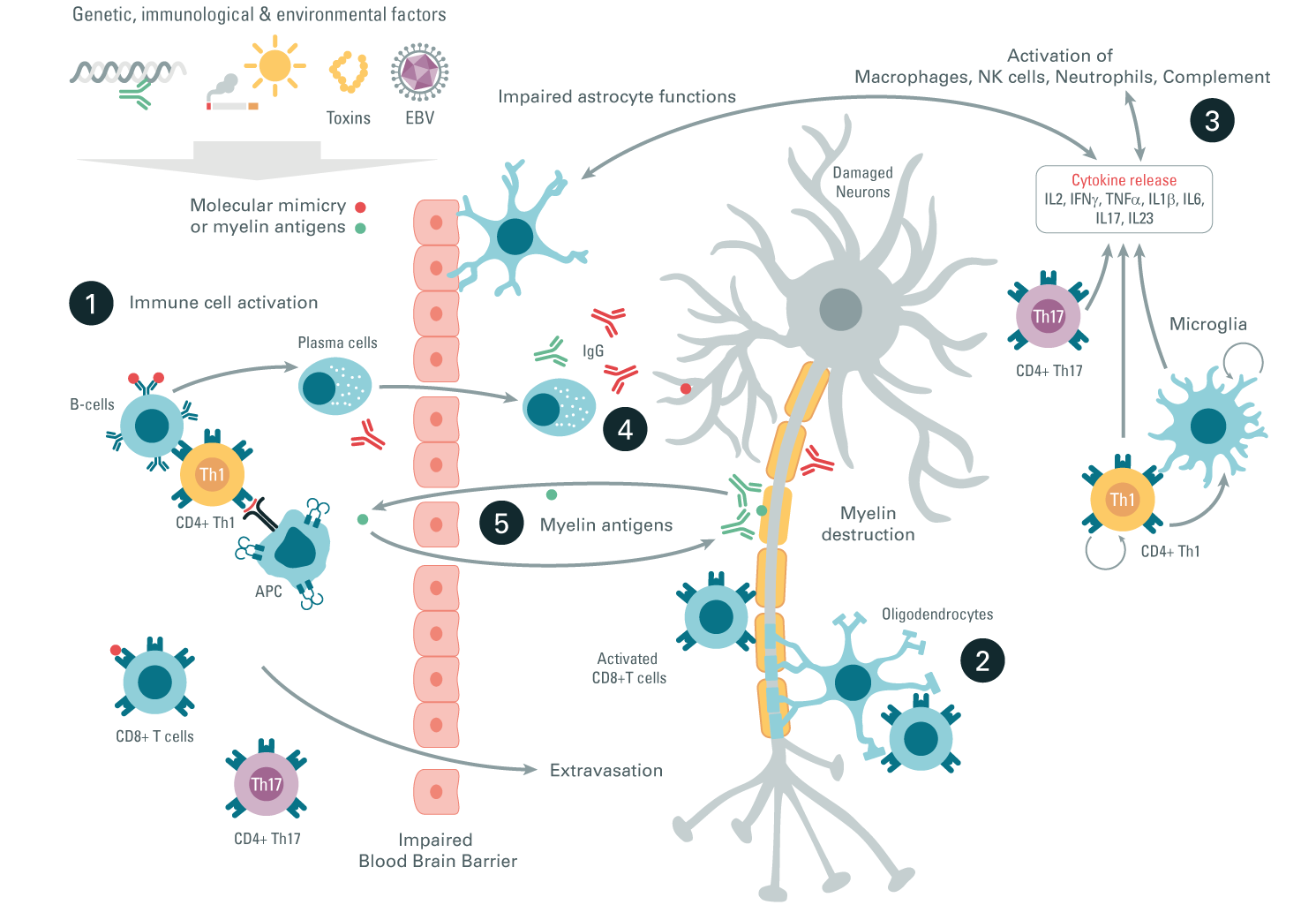
Step 1: Molecular mimicry (viral or bacterial peptides that share homology with brain proteins such as myelin) or myelin antigens are the antigens that induce immune activation. Activated Th1, Th17, and CD8+ peripheral T cells infiltrate the CNS where they secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Step 2: CD8+ cytotoxic T cells directly attack the oligodendrocytes and myelin, promoting their destruction.
Step 3: Activated microglia, macrophages, NK cells, or neutrophils participate in pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion and thereby contribute to neuronal damage and a demyelination process.
Step 4: Activated B cells secrete autoantibodies that amplify the CNS attack through complement activation or macrophages inducing neuron damage.
Step 5: A continuous myelin antigen release induces myelin autoantibody production and further amplifies the demyelinating circle.
Type 1 diabetes
Investigate the world of diabetes research
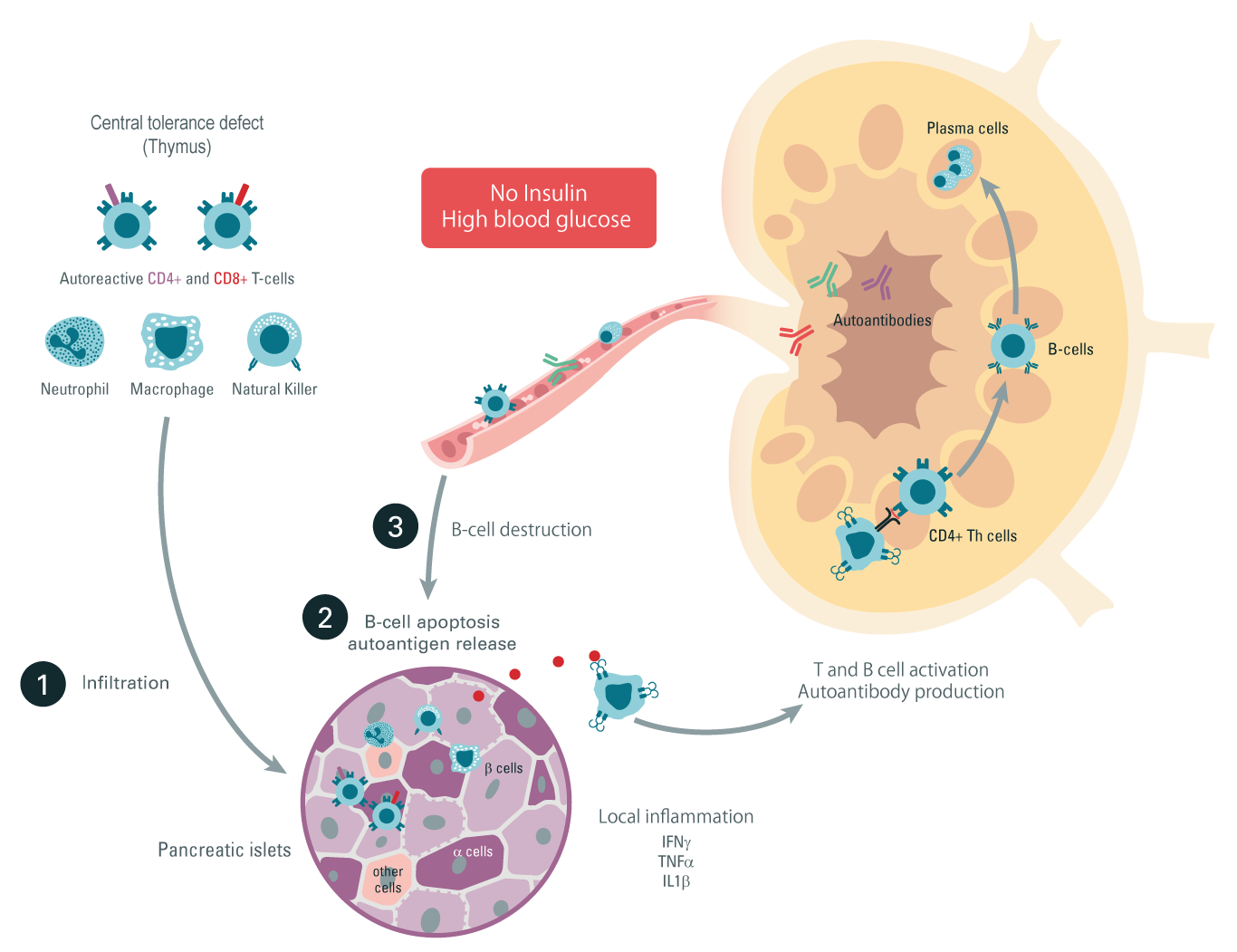
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune disease, albeit less common than its sibling Type 2 diabetes. Autoimmune diabetes represents 10% of diabetes patients and is the most common form affecting children under 15 years of age. Diabetes is characterized by high blood glucose levels due to pancreatic islet beta-cell destruction and insulin deficiency.
Type 1 diabetes inflammatory pathway
Step 1: Autoreactive T cells, neutrophils, NK cells, and macrophages infiltrate the beta-pancreatic islets, leading to inflammatory cytokine production and local inflammation.
Step 2: Autoantigens are liberated due to the pancreatic insulin producing β cell apoptosis. Those autoantigens are recognized by antigen-presenting cells and migrate to the lymph nodes.
Step 3: Activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, as well as autoantibody-producing differentiated B cells, leave the lymph node and migrate back to the pancreas, where they exert their cytotoxic activities leading to β-cell destruction and Type 1 diabetes.