
HTRF Human Total WRN Detection Kit, 10,000 assay points
HTRF Human Total WRN Detection Kit, 10,000 assay points


This HTRF kit allows for the cell-based quantitative detection of WRN.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Protein Quantification |
| Sample Volume | 16 µL |
This HTRF kit allows for the cell-based quantitative detection of WRN.


HTRF Human Total WRN Detection Kit, 10,000 assay points


HTRF Human Total WRN Detection Kit, 10,000 assay points


Product information
Overview
WRN is a protein of the helicase family involved in genome stability-related process including DNA repair, replication, and maintenance via telomere stability. Abnormal WRN functions characterize Werner Syndrome, which is a rare genetic disorder where genome stability is compromised, leading to the accumulation of senescence factors and premature aging in patients. As a disorder related to genome stability and degenerescence, it is also strongly related to increased cancer risks.
Specifications
| Application |
Protein Quantification
|
|---|---|
| Brand |
HTRF
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Lysis Buffer Compatibility |
Lysis Buffer 1
|
| Molecular Modification |
Total
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
16 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Target |
WRN
|
| Target Class |
Biomarkers
|
| Target Species |
Human
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Inflammation
Oncology
Rare Diseases
|
| Unit Size |
10,000 assay points
|
How it works
WRN assay principle
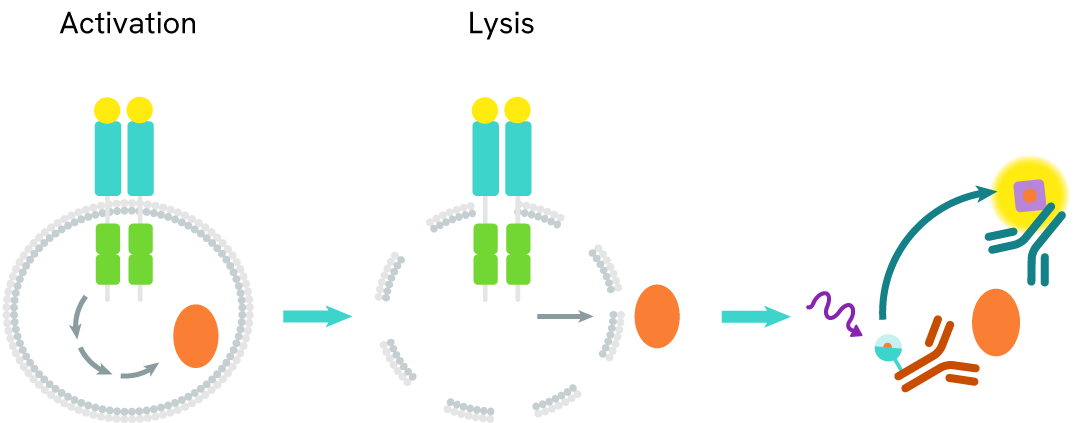
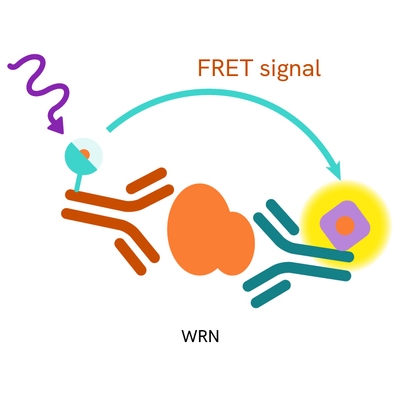
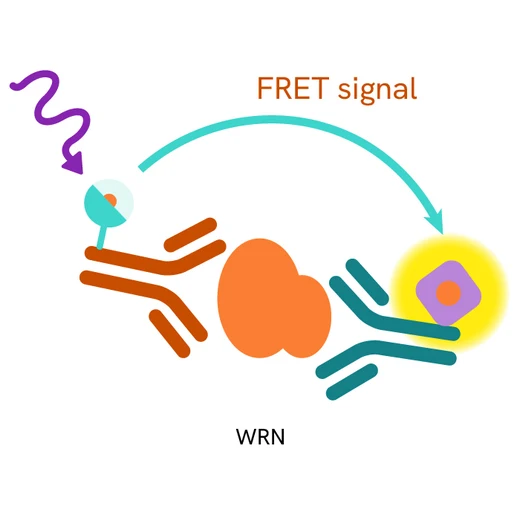
The WRN assay measures WRN levels in cells. Unlike Western Blot, the assay is entirely plate-based and does not require gels, electrophoresis, or transfer. The assay uses 2 antibodies, one labeled with a donor fluorophore and the other with an acceptor. In the presence of WRN, the labeled antibodies form an immune complex, bringing the donor fluorophore into close proximity to the acceptor and generating a FRET signal. The signal intensity is directly proportional to the concentration of total protein present in the sample.

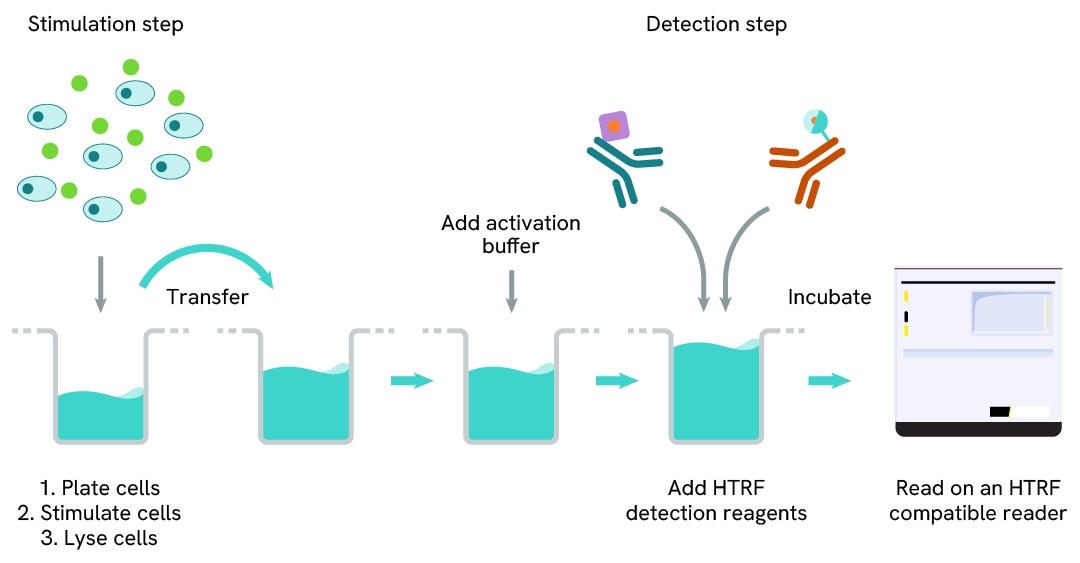
WRN two-plate assay protocol
The two-plate protocol involves culturing cells in a 96-well plate before lysis, then transferring lysates into a 384-well low volume detection plate before the addition of WRN HTRF detection reagents. This protocol enables the cells' viability and confluence to be monitored
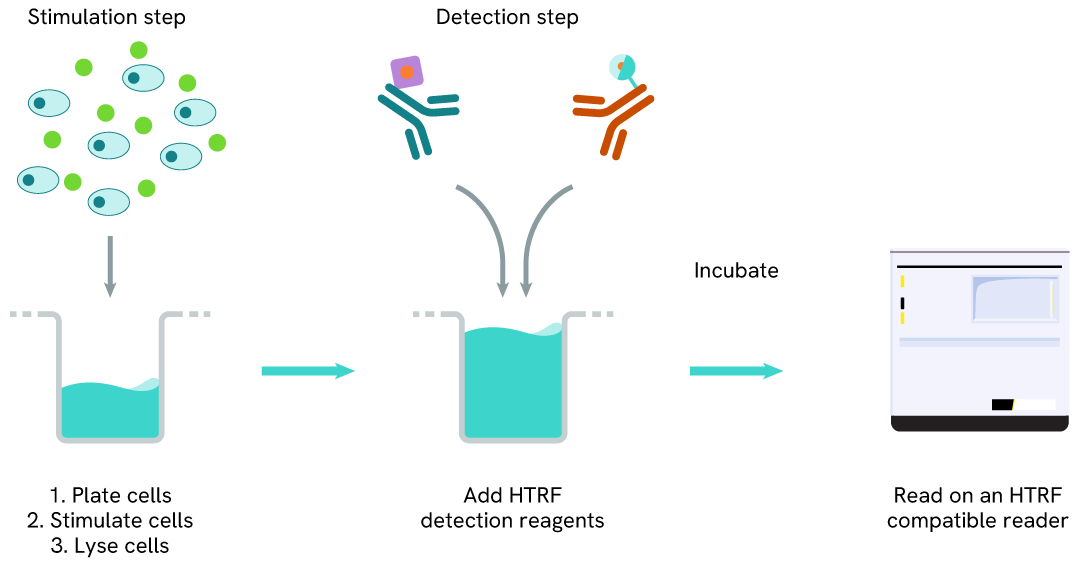
WRN one-plate assay protocol
Detection of WRN with HTRF reagents can be performed in a single plate used for culturing, stimulation, and lysis. No washing steps are required. This HTS designed protocol allows miniaturization while maintaining robust HTRF quality.
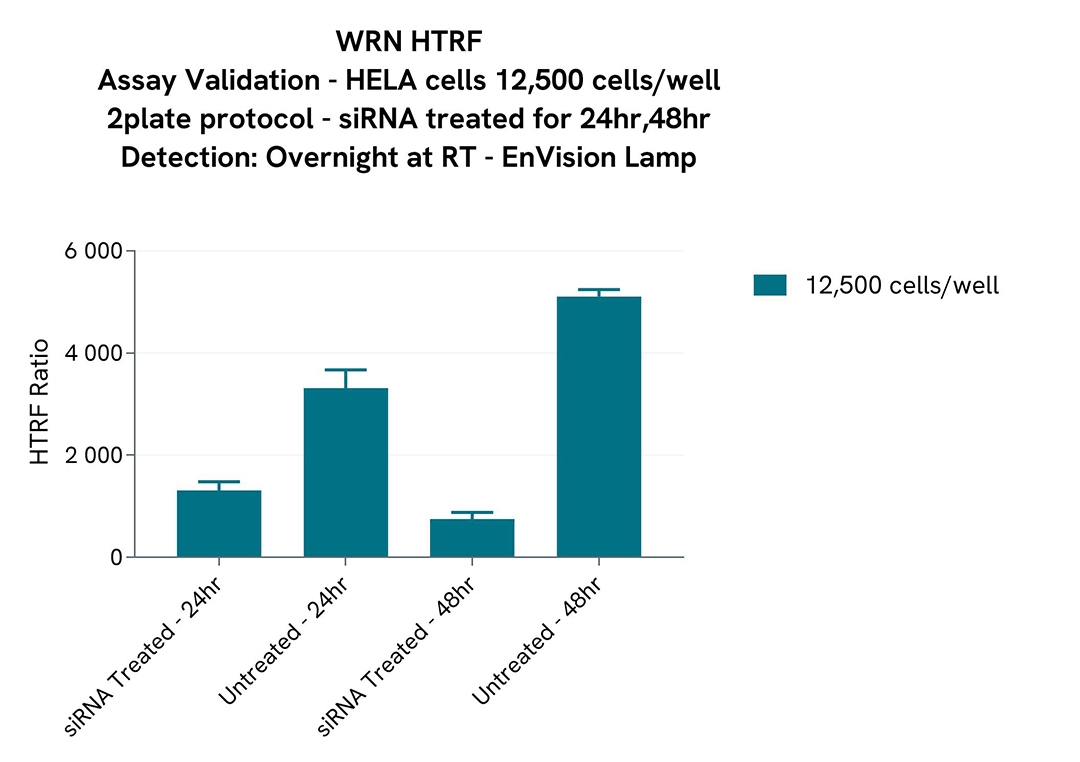
Assay validation
Assay Validation of WRN Detection with siRNA in HeLa cells
HELA cells were plated at 12,500 cells per well under 50 µL in a 96-well plates in complete culture medium. Cells were left to rest for 24hrs before treatment. The initial media was removed and cells were siRNA-treated by adding 50 µl of a mix of Transfection Reagent & siRNA for WRN. Cells were then incubated for 24hr and 48hr at 37°C, 5% CO2.
After incubation, the cells were lysed with 50µL of supplemented lysis buffer #1 at 1X for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking, and 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a low volume white microplate before the addition of 2 µL of the HTRF d2 detection reagent and 2 µL HTRF Eu-K detection reagent. The HTRF signal was recorded after ON incubation.
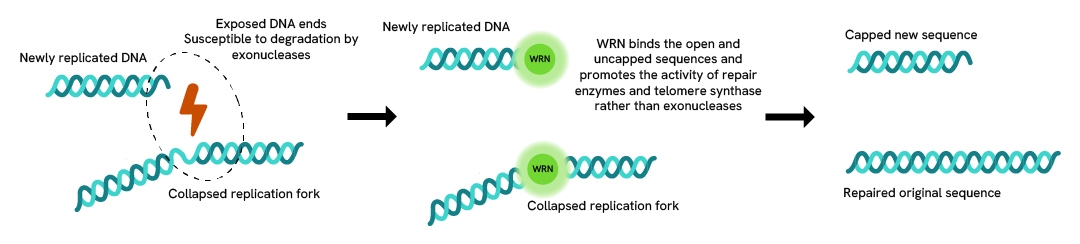
Simplified pathway
WRN signaling pathway
WRN recruitment takes place at collapsed replication forks of DNA breaks, where it becomes activated by cell cycle kinases like CDKs. There, it stabilizes and supports other helicases like RAD5 which keeps the DNA structure open for repair enzymes, but also downregulates the activity of exonucleases that could otherwise work along the exposed DNA strand and degrade it. This protects the replicated sequence as well as the original one. It also limits the occurrence of degenerated DNA because the genome goes through rounds of replication, thus protecting it from senescence.
If WRN is defective or under expressed, exonucleases are not prevented from degrading replication forks and the genome quickly ages.
Loading...


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.




































