
Bead mill homogenization and chemagic 360 automated DNA extraction workflow for High-Definition PCR detection of tick-borne pathogen
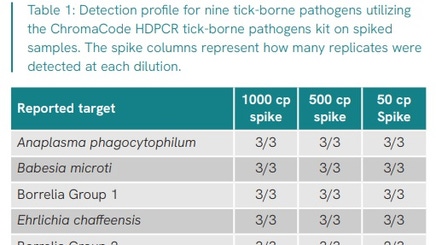
Ticks are considered one of the most dangerous arthropod vectors worldwide for the transmission of zoonotic infections, second only to mosquitoes. The increasing burden of tick-borne disease has prompted numerous public health efforts for research around mitigation and epidemiological surveillance, to better characterize pathogen burden in a given population. In this application note, whole ticks were mechanical disrupted via bead-beating on the Omni Bead Ruptor Elite bead mill homogenizer, spiked with known copy numbers of pathogen control DNA, and taken through an automated nucleic acid extraction on the chemagic 360 extractor. Resulting eluates were taken through the high-definition PCR (HDPCR™) tick-borne pathogen (TBP) research panel to assess extraction efficiency.
Download the full application note to review protocols for dry-grinding whole ticks and detection profiles for all nine pathogens spiked controls and copy number ranges.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
To view the full content please answer a few questions
Download Resource
Bead mill homogenization and chemagic 360 automated DNA extraction workflow for High-Definition PCR detection of tick-borne pathogen




























