Ad19a/64 vector for vaccination
Our proprietary Ad19a/64 vector (Subtype D) can be used to overcome the low transduction efficiency of commonly used adenovirus (Ad) serotypes and help overcome the challenge of pre-existing immunity against commonly used adenovirus serotypes. It is an attractive alternative for the most commonly used human adenovirus type 5 (Ad5) for specific types of applications.
This adenoviral vaccine vector demonstrates a higher transduction efficiency in various human cells (e.g., dendritic cells, cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts, PBMCs, myoblasts, and myotubes) compared to Ad5, as supported by preclinical data. It also possesses CAR-independent binding properties, targeting sialic acid-dependent receptors. Preclinical research vaccine studies in non-human primates, indicate that the vector may potentially enhance CD4 and CD8 immune responses.
Key benefits of our Ad19a/64 adenoviral vaccine vector
- Efficient gene transfer to human DCs and skeletal muscle cells
- Low seroprevalence within the human population
- Transduction experiments with human myoblasts and primary myotubes
Here we share some data to demonstrate how the Ad19a/64 vector transduces human myoblasts and primary myotubes.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.

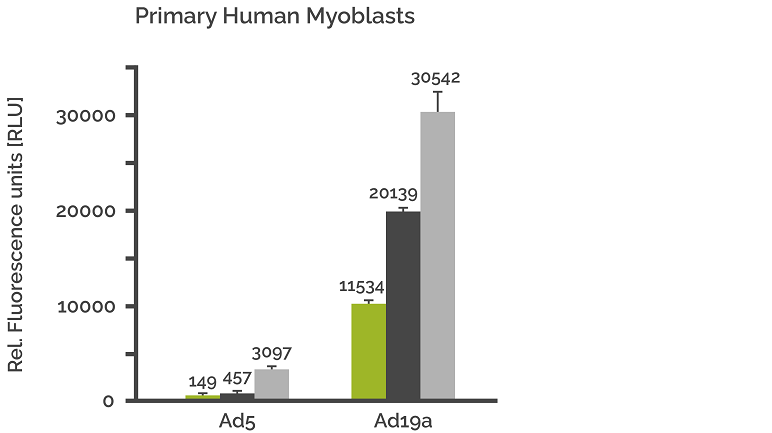
Transduction of myoblasts with Ad5-EGFP (Ad5) and Ad19a/64-EGFP (Ad19a)
Primary myoblasts of human ape, pig, and mouse origin were transduced with 1250 VP/cell (green columns), 2500 VP/cell (black columns), and 12500 VP/cell (grey columns) respectively, and GFP expression was quantified after 48 hr. Each value represents the mean of transgene expression per well in relative light units (RLU) from five independent experiments +/- SD.
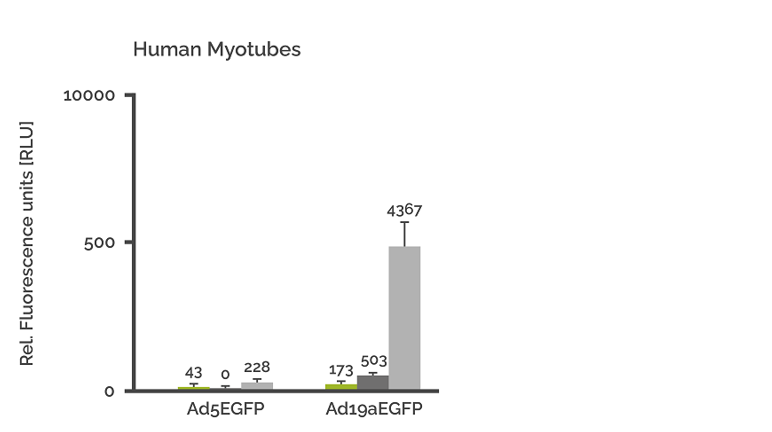
Transduction of primary myotubes (MTs) with Ad5EGFP and Ad19a/64-EGFP
Ten-day-old human myotubes were transduced with 1250 VP/cell (green columns). 2500 VP/cell (black columns) and 12500 VP/cell (grey columns), respectively. GFP expression was quantified after 48 hrs. Each value represents the mean relative light units (RLU) of five independent transductions +/- SD
Ad19a/64 in mucosal boost immunization against SARS-CoV-2
In the course of the worldwide pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2, Ad19a/64 was used to administer Spike S protein intranasally in mice. After plasmid DNA or mRNA priming before intranasal immunization, the group saw a strong systemic and mucosal immune reaction triggered by Ad19a/64. The intranasal boost strategies lead to strong protection against a SARS-CoV-2 infection in mice. The data suggests that mucosal booster immunizations after mRNA priming is a promising approach to establish mucosal immunity in addition to systemic responses.
Reference:
Lapuente, D., Fuchs, J., Willar, J. et al. Protective mucosal immunity against SARS-CoV-2 after heterologous systemic prime-mucosal boost immunization. Nat Commun 12, 6871 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27063-4
Licensing information
Custom Ad19a/64 vectors are available for research use under a limited use license. Clinical and commercial use requires a license. Please contact us to speak with our licensing team if you’re interested in this technology.