Introduction to cell viability measurement
Since the quality of the cell sample is vital for potential downstream experiments, viability measurements are routinely performed in many laboratories. Choosing the correct method for conducting cell viability measurement is essential for obtaining consistent and reliable results. Here we review a common method for measuring cell viability: acridine orange/propidium iodide.
Using acridine orange/propidium iodide (AO/PI) to measure cell viability
Acridine orange (AO) and propidium iodide (PI) are nucleic acid binding dyes that can be used to measure the cell viability. Since AO is cell permeable, all stained nucleated cells generate a green fluorescence. PI (~668 Daltons) only enters cells with compromised membranes and therefore dying, dead, and necrotic nucleated cells stained with PI generate a red fluorescence. When cells are stained with both AO and PI, live nucleated cells only fluoresce green and dead nucleated cells only fluoresce red. This is due to Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET), where the PI signal absorbs the AO signal producing no spill-over or double positive results. Additionally, other membrane-exclusion viability dyes such as: ethidium bromide (EB), 7AAD, SYTOX green/red, DRAQ5 and others may also be used instead of PI. Cell viability is calculated by examining the ratio of the number of live to the number of dead fluorescing cells. This assay can not only be used to measure the viability of nucleated cells in cell culture and purified samples but also in complex samples such as PBMC, whole blood, bone marrow, bronchoalveolar lavage, tumor digests, primary samples and many more.

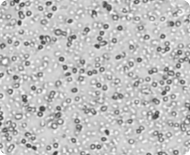
Brightfield image of a peripheral blood sample
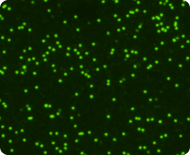
Live nucleated cells stained with Acridine Orange

Dead nucleated cells stained with Propidium Iodide
AO/PI protocol: sample preparation and analysis
Simple, user-friendly Cellometer procedure
With the Cellometer™, Auto 2000, K2 and Ascend, 20µl of sample is added to the Cellometer counting chamber in the disposable slide. Imaging and analysis of the samples is completed in less than 30 seconds. Brightfield and fluorescent cell images can be viewed to check cell morphology and verify cell counting. Total cell count, concentration, and mean diameter are automatically displayed.
AO/PI protocol
- Obtain Revvity AO/PI solution
- Stain cell sample at 1:1 with AO/PI solution
- Load counting chamber slide and analyze

1. Pipette 20 µl of sample into a disposable slide (or 10 µl if using the 8-chamber slide with the Cellometer Ascend instrument)

2. Insert slide into the instrument
3. Select assay from a dropdown menu
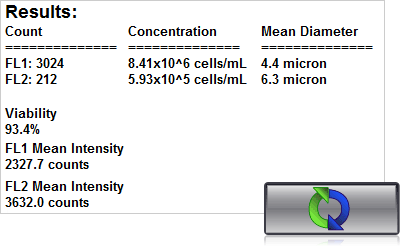
4. Click count, acquire image and view cell count, concentration, diameter
Viability measurement for messy samples using AO/PI
Tumor digest samples
Tumor digest samples are collected at the primary source of the tumor. Solid tumors are first digested and processed before they are utilized in experiments. These are inherently messy samples. They may contain tissue fragments and cellular debris making it difficult to identify and count cells of interest. With AO/PI only the nucleated cells are stained and analyzed.
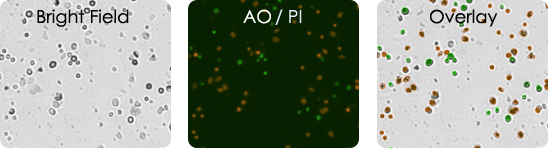
Tumor digest images
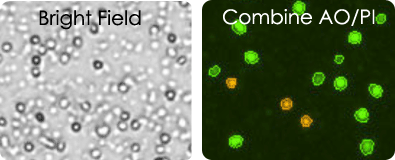
Leuko Pak images

Cord blood images
Both Leuko Pak and Cord blood samples contain a large amount of red blood cells, platelets and cell debris making it impossible to count in brightfield. Using AO/PI the concentration and viability of mononuclear cells can be measured.
Viability measurement in PBMCs
The quality of peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) samples after isolation, during experimentation, as well as before and after cryopreservation needs to be assessed. The two micrographs (right) show live mononuclear cells stained with acridine orange in green, and dead cells stained with PI in red.
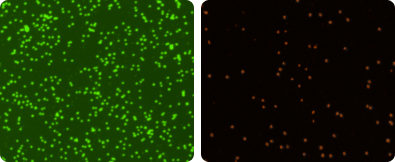
PBMC images
Conclusions & Cellometer selection guide
The Cellometer line of instruments can quickly and reliably obtain the viability of the cell sample by Trypan blue or fluorescent methods. Additionally, the system automatically reports a reliable cell count, concentration, and cell size in a single 20 µl assay. The fluorescent based Cellometer instruments (Auto 2000, K2 and Ascend) also allow researcher to count the total number of nucleated cells in a fresh clinical sample without the need to lyse red blood cells. The table below outlines the compatibility of Cellometer instruments and assay used for each selected application.
| Cellometer Auto T4 | Cellometer Auto 2000 | Cellometer Ascend | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purified cells– no debris | TB | TB or AOPI | TB or AOPI |
| Isolated MNCs – without lysing RBCs | NR | AOPI | AOPI |
| Fresh BM, CB, WB, MNCs w/ lysing of RBCs | TB | TB or AOPI | AOPI |
| Fresh BM, CB, WB without lysing | NR | AOPI | AOPI |
| Frozen BM, CB, WB | TB | TB or AOPI | AOPI |
| Digested tumors and BAL with tissue/cellular debris | NR | AOPI | AOPI |
AOPI = Acridine Orange/Prodidium Iodide, TB = Trypan Blue, NR = not recommended, BM = Bone Marrow, CB = Cord Blood, WB = Whole Blood, MNCs = Mononuclear cells
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.




























