Overview
The table below shows results from a compound interference study. We tested a panel of 24 compounds in a QC assay using our AlphaLISA™ toolbox bead products. The information below can be used for guidance as to what buffer components might interfere with AlphaLISA assays using Nickel Chelate NTA Acceptor beads, and at what concentrations interference might occur. These data are derived from single experiments and should serve more as a guide rather than a precise value, as it is unlikely you will be using the exact same assay design as used to generate the data below. Interference concentrations may vary depending on the assay components. It is possible your assay will tolerate higher or lower concentration than what is shown.
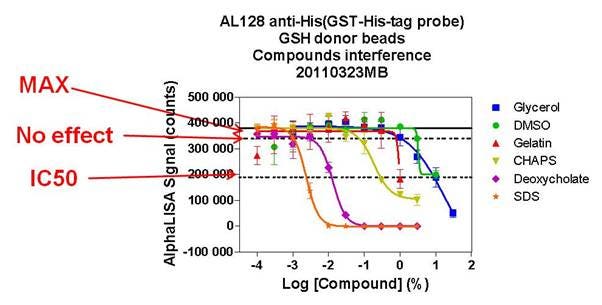
| No effect (10%) | 50% loss | Tested up to | % inhibition at Max | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycerol | % | 0.2 | 5.2 | 30% | 87 |
| DMSO | % | 0.05 | 0.4 | 10% | 95 |
| CHAPS | % | 0.02 | 0.1 | 3% | 90 |
| Deoxycholate | % | 0.005 | 0.02 | 3% | 94 |
| SDS | % | 0.08 | 0.01 | 3% | 98 |
| Triton X-100 | % | >3 | >3 | 3% | 0 |
| Tween 20 | % | >3 | >3 | 3% | 0 |
| TRIS (pH8.0) | M | 1.1E-02 | 1.3E-02 | 0.5M | 100 |
| 2-Mercaptoethanol | M | 5.5E-04 | 1.6E-02 | 0.1M | 90 |
| DTT | M | 8.7E-05 | 1.6E-03 | 0.1M | 99 |
| EDTA | M | 2.5E-06 | 4.0E-06 | 0.1M | 100 |
| EGTA | M | 2.6E-06 | 8.4E-06 | 0.1M | 100 |
| Imidazole | M | 1.1E-04 | 3.7E-04 | 0.1M | 100 |
| Mg2+ (MgCl2) | M | 1.0E-03 | 1.2E-02 | 0.1M | 95 |
| Urea | M | >0.1 | >0.1 | 0.1M | 0 |
| Vanadate | M | 7.3E-03 | 9.0E-03 | 0.1M | 100 |
| Citrate | M | 1.2E-05 | 4.5E-05 | 0.1M | 99 |
| Adenosine (ATP) | M | 1.6E-05 | 6.8E-05 | 0.01M | 100 |
| Glycine | M | 2.2E-05 | 1.5E-04 | 0.01M | 100 |
| NaF | M | >0.01 | >0.01 | 0.01M | 0 |
| Complete Protease Inhibitor | X | not determined | not determined | IX | 79 |
The table above indicates that an assay testing the effect of EDTA using Nickel chelate AlphaLISA Acceptor beads, streptavidin Alpha Donor beads, and biotin-His probe showed little effect on the assay signal at final EDTA concentrations up to 2.5 uM. EDTA did show a half-maximal inhibition of signal when used at a final concentration of 4.0 uM. When 0.1M EDTA was included in the assay, 100% signal inhibition was observed.

Figure: Key for how the values in our interference tables are derived. The “no effect” concentration was obtained by extrapolating the MAX - 10% MAX counts. Refer to the table above for actual interference values for each toolbox bead product.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
The information provided above is solely for informational and research purposes only. Revvity assumes no liability or responsibility for any injuries, losses, or damages resulting from the use or misuse of the provided information, and Revvity assumes no liability for any outcomes resulting from the use or misuse of any recommendations. The information is provided on an "as is" basis without warranties of any kind. Users are responsible for determining the suitability of any recommendations for the user’s particular research. Any recommendations provided by Revvity should not be considered a substitute for a user’s own professional judgment.




























