Overview
The skeleton plays a critical structural role in vertebrates. An understanding of bone biology is critical in the development of new therapeutics for osteoporosis, bone metastasis, and bone healing. In vivo and ex vivo imaging can be used to study bone development, bone loss, bone metastasis, and bone healing and repair.
Bone diseases such as osteoporosis can cause bones to become brittle and weak, resulting in fractures that can lead to long-term pain and limit mobility. Metastasis of breast and other cancers to bone can also cause significant pain and morbidity due to osteolysis and bone resorption.
Revvity offers IVISense™ near-infrared fluorescent (NIRF) probes for imaging bone biology, as well as IVISbrite™ bioluminescent tumor cell lines for imaging metastasis in vivo.
Products for imaging bone biology
- IVISense Cat K 680 FAST is a NIRF probe that detects cathepsin K (Cat K) activity. Cat K is expressed in osteoclasts, chrondrocytes, and synovial fibroblasts and is critically involved in bone resorption and collagen degradation. Cat K is useful in pathological models, such as Osteoporosis, where bone resorption and soft tissue calcification occurs.
- IVISense Osteo is a NIRF probe that binds to and detects exposed hydroxyapatite, a bone mineral seen during bone turnover. Due to its specificity this probe is a marker of bone turnover during bone growth and/or bone healing.
- Our bioluminescent IVISbrite tumor cell lines are stably transfected with a luciferase (luc or luc2) reporter gene that allows you to visualize the growth of the cells in vivo. These cell lines are injected into an appropriate mouse model to monitor early tumor development, monitor tumor growth and metastases, quantify tumor burden in a whole animal model, and follow therapeutic responses non-invasively.
Mouse model for bone biology
Bone growth and healing
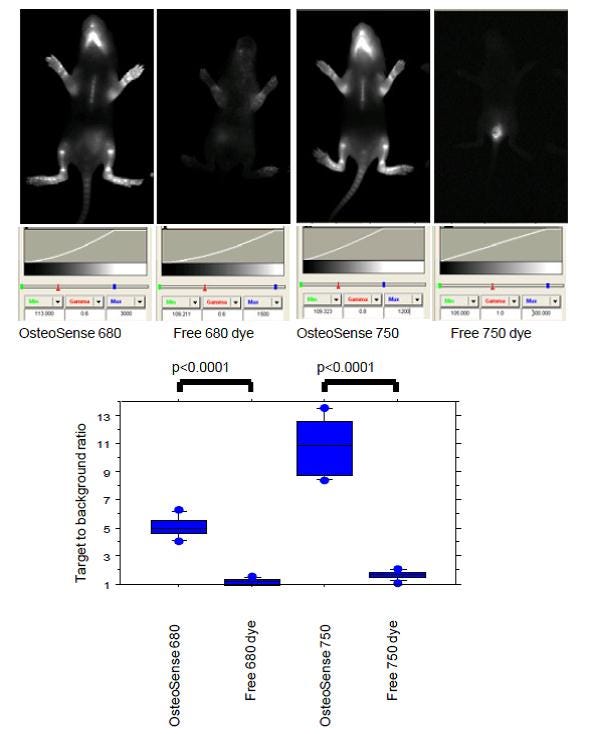
IVISense Osteo 680, IVISense Osteo 750 or free dyes (0.5 nmoles) were injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) in 1 week-old Balb/c mice. Imaging was performed 24 hrs later a planar Kodak 2000 MM system (. 4 x 15 sec acquisition ) using appropriate filter sets. Regions of interest were drawn within the visible tibias and lower jaws. Target to background ratio was defined as the fluorescent signal (in RFU, relative fluorescent units) divided by the adjacent tissue background signal. Statistical analysis of in vivo bone-associated fluorescence was conducted using a two-tailed unpaired Student t-test.

Figure 1. IVISense Osteo (formerly OsteoSense) highlights areas of active bone remodeling
Bone metastasis
Selected citations for bone metastasis:
- Hu, Z. et al. Oncolytic adenovirus expressing soluble TGFβ receptor II-Fc-mediated inhibition of established bone metastases: a safe and effective systemic therapeutic approach for breast cancer. Mol. Ther. 19, 1609–1618 (2011). Link
- Takeshita, F. et al. Efficient delivery of small interfering RNA to bone-metastatic tumors by using atelocollagen in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 12177–12182 (2005). Link
- Thudi, N. K. et al. Zoledronic acid decreased osteolysis but not bone metastasis in a nude mouse model of canine prostate cancer with mixed bone lesions. Prostate 68, 1116–1125 (2008). Link
- Tu, Q. et al. Targeted overexpression of BSP in osteoclasts promotes bone metastasis of breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 218, 135–145 (2009). Link
Osteoporosis
OVX Rat model: estrogen-induced osteoporosis, close representation of osteoporosis in humans. In this model, IVISense Cat K FAST detects an increase in cathepsin k activity while hydroxyapatite signal remains stable.
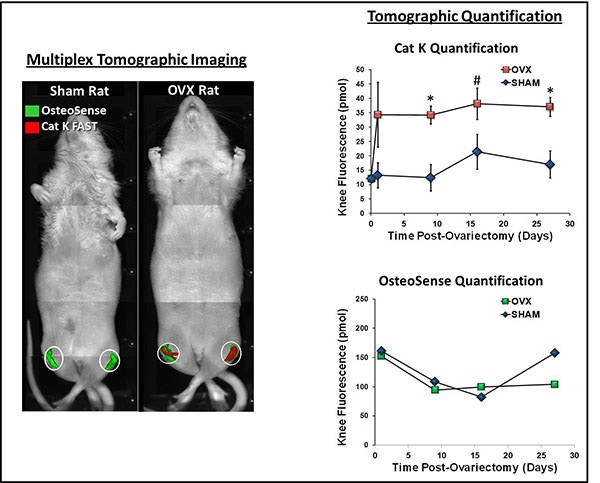
Figure 2. Sprague Dawley rats (Charles River Laboratories) were ovariectomized and depilated to allow imaging of the lower torso and legs by fluorescence tomography. Rats were injected intravenously with IVISense Cat K 680 FAST and IVISense Osteo 750 for imaging 24h later. For subsequent time points, rats were pre-imaged and then re-injected with imaging probes for imaging 24h later. IVISense Osteo quantification was determined by subtraction of pre-image results. Graphs show no difference in IVISense Osteo incorporation into the knee region, however a significant increase in IVISense Cat K FAST signal was seen as early as one day post-surgery. Symbols indicate statistical significance (*p < 0.01, # p < 0.05).
Application notes and posters
- Poster: Development of a Fast-Activating New Near Infrared-Labeled Probe for Detecting Cathepsin K Activity
- Poster: Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging of Bone Remodeling using IVISense Osteo
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.




























